Difference between revisions of "Junctions"
From Mashinky
(Added Y Junctions) |
m |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
All the exaples below have the basic signaling shown on the images, better signalling positions can improve their preformance if nessesary. | All the exaples below have the basic signaling shown on the images, better signalling positions can improve their preformance if nessesary. | ||
| − | + | ==Y Junctions== | |
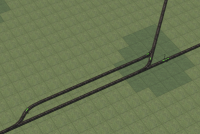
Y-Junctions act as a convergence or divergence points between two routes on a railway line. Simple solutions tend to work well, but tend to have significant drawbacks when used at high capacity. | Y-Junctions act as a convergence or divergence points between two routes on a railway line. Simple solutions tend to work well, but tend to have significant drawbacks when used at high capacity. | ||
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
| − | + | ==Terminus Junctions== | |
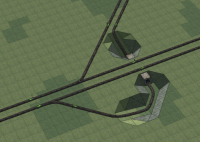
These are a selection of junctions that go at the end of a railway line, these are deigned for both high capacity and the ability to turn the trains arround to prevent the locomotives from reversing on their return journey. | These are a selection of junctions that go at the end of a railway line, these are deigned for both high capacity and the ability to turn the trains arround to prevent the locomotives from reversing on their return journey. | ||
Revision as of 18:55, 16 October 2017
All the exaples below have the basic signaling shown on the images, better signalling positions can improve their preformance if nessesary.
Y Junctions
Y-Junctions act as a convergence or divergence points between two routes on a railway line. Simple solutions tend to work well, but tend to have significant drawbacks when used at high capacity.
Terminus Junctions
These are a selection of junctions that go at the end of a railway line, these are deigned for both high capacity and the ability to turn the trains arround to prevent the locomotives from reversing on their return journey.